Table of Content
If you prefer, you can also click Browse and then navigate to the desired path. To get started, right-click on the Computer or This PC icon on the desktop and select Properties. If you don’t have that icon on your desktop already, you can add any missing desktop icons easily. For some reason, if, after you’ve set the PATH variable, you want to unset it, you can do so using the following steps.
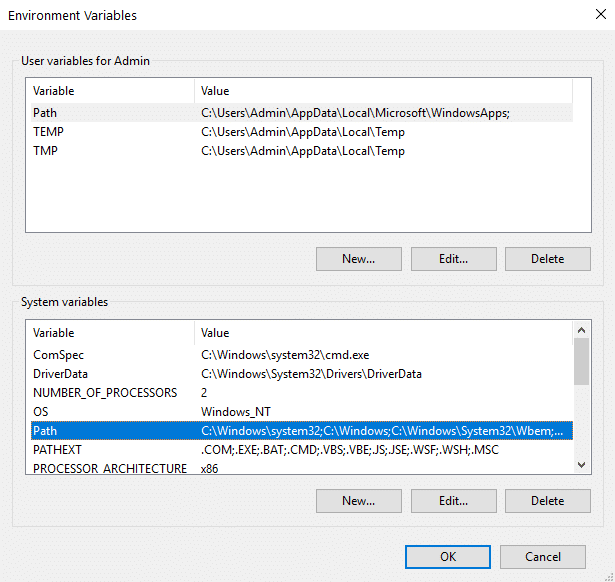
Tap on the entry you want to remove to select it and hit the Delete button on the right. On older versions of Windows, you can click the Edit text button and delete the recent PATH entry for the Variable value text field. In System Properties, tap on the Advanced tab and click the Environment Variables button at the bottom.
How do I edit the PATH variable?
On Unix-like operating systems, environment variable names are case sensitive, but they are not on DOS, OS/2, and Windows. In general, the collection of environment variables function as an associative array where both the keys and values are strings. The interpretation of characters in either string differs among systems. When data structures such as lists need to be represented, it is common to use a colon (common on Unix and Unix-like) or semicolon-deliminated list.
In the Edit System Variable dialog box, click inside the Variable value text box to modify the path by specifying the directory where the executable program are located. If you don't have the item PATH, you may select to add a new variable and add PATH as the name and the location of the directory where the executable program is located as the value. Once a matching executable file is found, the system spawns a new process which runs it.
How to set the path and environment variables in Windows
A default of /Y can be overridden by supplying the /-Y switch on the command line. The /Y switch instructs the command to replace existing files without prompting for confirmation. Unset is a builtin command implemented by both the Bourne shell family (sh, ksh, bash, etc.) and the C shell family (csh, tcsh, etc.) of Unix command line shells. It unsets a shell variable, removing it from memory and the shell's exported environment. It is implemented as a shell builtin, because it directly manipulates the internals of the shell.
You’ll know you’re on your path when you see yourself taking steps into new territory. Alternatively, we can choose the install folder by clicking on the Browse Directory… button. Let’s see the steps to set the variable on Windows. %CMDEXTVERSION%This pseudo-variable expands to the version of the command-line extensions of CMD.EXE, if enabled (e.g. "1" under Windows NT, "2" under Windows 2000 and Windows XP).
Install Oracle 19c Database On Windows 10
Just make sure it doesn’t interfere with the higher-priority programs. If you type charmap into the command line, you’ll get a massive list of Unicode characters you can copy and use, for example. “notepad” runs Notepad, “msinfo32” gets you a list of your computer’s specs, and so on.
These are values that are fetched like environment variables, but are not truly stored in the environment but computed when requested. %$WIDTH%Used by DOS Plus to define the screen width of the console in columns. This is used to control in a portable way the formatting of the screen output of commands like DIR /W or TYPE filename. See also the related environment variables %$LENGTH% and %DIRSIZE% as well as the similar pseudo-variable %_COLUMNS%.
What is the path command?
This always worked with NETX, but it will also work with Personal NetWare's ODI/VLM if the current drive is a PNW-mapped drive . See also the similarly named environment variable %LOGINNAME%. %_ROWS%This pseudo-variable returns the current number of screen rows depending on the display mode, f.e. This variable was originally introduced by 4DOS, but also became available with COMMAND.COM since DR-DOS 7.02.
They are usually referenced by putting special symbols in front of or around the variable name. Use this check after adding a new path to be sure it has been set. If you already know the path, just write it in or copy and paste it.
It assists the system in determining where to install files, locate programs, and check for user and system preferences. It may also be accessed from anywhere on the computer by graphical and command-line tools. It is required to set up the environment variables so that system knows the executable file that it needs to run on a given command. Environment variables store data about a system’s environment so the system knows where to look for certain information. The PATH variable is one of the most well-known environment variables since it exists on Windows, Mac, and Linux machines and does a fairly user-facing job on all. Its actual form is just a text string containing a list of directory paths that the system will search every time you request a program.

The following commands can also be used, but are often dependent on a certain shell. Using "Browse Directory", you can select a directory. While adding directories to the path is simple, don't remove any existing path directories. While this guide is focused on Windows 10, it’s important to note that these variables will also work on Windows 8.1, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows 11.
%DIRCMD% is also supported by the external SDIR.COM/DIR.COM Stacker commands under Novell DOS 7 and higher. Shell scripts and batch files use environment variables to communicate data and preferences to child processes. They can also be used to store temporary values for reference later in a shell script. However, in Unix, non-exported variables are preferred for this as they don't leak outside the process. The PATH variable is nothing more than a directory of your computer's applications and instructions.
In this article, we will see how we can create and set up path environment variables in Windows 11. In this article, I will let you know about ways by which you can add or edit the path environment variable in windows 11. While both approaches let you execute programs or commands via the CLI , they aren’t very efficient. A better solution here is to set the PATH variable for those programs or commands in the environment variable so you can access them from anywhere on the file system hierarchy.
Setting the path and environment variables differs depending on the Windows operating system version on your computer. Select a link below for your version of Windows and follow the steps. %SECOND%This pseudo-variable returns the seconds of the current time in a 2-digit format with leading zeros, f.e. It resembles an identically named identifier variable in Novell NetWare login scripts. %MINUTE%This pseudo-variable returns the minutes of the current time in a 2-digit format with leading zeros, f.e "00".."59". %HOUR24%This pseudo-variable returns the hours of the current time in 24-hour format in a 2-digit format with leading zeros, f.e.

This will bring up the System Properties dialog, which should already be open to the Advanced tab. Go ahead and click on the Environment Variables button at the very bottom. In System Properties, go to the Advanced tab and click on the Environment Variables button at the bottom. Next, in the field beside Open, type in sysdm.cpl and press Enter or click OK to open System Properties. If you’re wondering why you’d want to set the PATH variable and how to do it, here’s a guide explaining the same in detail. Connect and share knowledge within a single location that is structured and easy to search.

No comments:
Post a Comment